Qemu
m (→Possible emulation guest targets) |
m (→HP-UX) |
||
| (99 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == QEMU | + | == QEMU for PA-RISC overview == |
| − | + | '''Important: Please run at least QEMU version 8.0.0'''.<br> | |
| − | + | QEMU versions prior to v7.1.0 had various strange bugs. 64-bit CPU emulation requires at least QEMU version 8.2. | |
| − | + | QEMU can emulate two different machines: | |
| − | + | * a 32-bit [https://www.openpa.net/systems/hp-visualize_b132l_b160l_b180l.html HP B160L desktop] with up to 16 concurrent PA7100LC CPUs (SMP), and | |
| + | * a 64-bit [https://www.openpa.net/systems/hp-visualize_b1000_c3000_c3600.html HP C3700 workstation] with up to 16 concurrent PA8700 CPUs (SMP). | ||
| + | Use the QEMU ''-machine B160L'' (for a 32-bit machine) or ''-machine C3700'' (for a 64-bit machine) option to boot. | ||
| + | Various operating systems are supported, e.g. Linux, HP-UX and BSD variants. For details please check the sections below. | ||
| + | PA-RISC machines need a firmware ("PDC" = Processor Dependend Code), and QEMU comes with a precompiled firmware which is based on a [https://github.com/hdeller/seabios-hppa/ fork of SeaBIOS]. | ||
| − | + | QEMU for PA-RISC has been developed by: | |
| + | * [mailto:rth@twiddle.net Richard Henderson]: QEMU CPU emulation, QEMU hardware drivers | ||
| + | * [mailto:deller@gmx.de Helge Deller]: QEMU hardware drivers, SeaBIOS PDC firmware, CPU emulation bug fixes, QEMU linux-user | ||
| + | * [mailto:svens@stackframe.org Sven Schnelle]: Lots of fixes in QEMU and SeaBIOS (SCSI, CPU emulation fixes, SeaBIOS PDC firmware) | ||
| + | QEMU for PA-RISC can be further developed via paid contract from: | ||
| + | * [mailto:mark.cave-ayland@ilande.co.uk Mark Cave-Ayland]: offers paid contract work on QEMU for PA-RISC | ||
| − | + | == QEMU supported guest operating systems == | |
| − | QEMU | + | QEMU does support those operating systems as guests: |
| − | * [ | + | * Linux (Debian, Gentoo) |
| − | * [ | + | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HP-UX HP-UX], versions 9.x up to 11.11 |
| − | * [ | + | * [https://wiki.netbsd.org/ports/hppa/ NetBSD], >= 8.0 |
| + | * [https://winworldpc.com/product/nextstep/3x NextSTEP] | ||
| + | * [ftp://ftp.cirr.com/pub/hppa/mklinux/ OSF/MkLinux] | ||
| − | == | + | == QEMU command line options == |
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| − | + | |+ Standard qemu options: | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | ! scope="col" | Qemu command line option | |
| − | + | ! scope="col" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | -machine C3700 | |
| + | | start a 64-bit C3700 workstation (qemu >= v8.2) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -machine B160L | ||
| + | | start a 32-bit B160L workstation (default) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -smp cpus=4 | ||
| + | | define number of CPUs in the guest (maximum CPUs: 32) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -m 1G | ||
| + | | tell machine to have 1G of RAM memory | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -accel tcg,thread=multi | ||
| + | | always use this to enable parallel tcg (otherwise all guest CPUs run on one host CPU) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -boot menu=on | ||
| + | | Firmware: enable interactive mode (same as "BOOT PRI '''IPL'''") | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -boot order=c | ||
| + | | Firmware: Boot from first hard disc | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -boot order=d | ||
| + | | Firmware: Boot from first CD/DVD | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -boot order=g-m | ||
| + | | Firmware: Boot from SCSI ID0 ("g"), SCSI ID1 ("h"), ... SCSI ID7 ("m") | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -serial mon:stdio | ||
| + | | multiplex serial console to stdout (you want to enable this option!) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -nographic | ||
| + | | disable artist graphic card emulation, so no graphics output | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -display sdl | ||
| + | | if you need graphics you should prefer SDL display output if your run Qemu < v2.0. In previous qemu versions, GTK had a bug which slows down output. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -vnc :1 | ||
| + | | start graphics output on VNC output, connect to ''hostname'':1 with any VNC viewer | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | --nodefaults | ||
| + | | create an empty machine without default SCSI or network controller (qemu >= v8.2). Add "-serial mon:stdio" to get a serial console, otherwise no output will be visible. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+ HPPA specific qemu options: | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Qemu command line option | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -global artist.width=800<br>-global artist.height=600 | ||
| + | | set Artist graphic card to 800x600 pixel | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -fw_cfg opt/pdc_debug,string=255 | ||
| + | | enable all firmware debug infos (1: show PDC calls, 2: show IODC calls) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -fw_cfg opt/hostid,string=334455 | ||
| + | | set the hostid to ''334455'' (instead of the default value ''2006243326''). Visible in Linux in /proc/cpuinfo, and with "uname -i" in HP/UX | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -fw_cfg opt/console,string=[serial or graphics] | ||
| + | | set default firmware output method to serial or graphics console. When selecting serial, you need to add e.g. "-serial mon:stdio" too. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -fw_cfg opt/font,string=[1-4] | ||
| + | | select default graphics font: HP 8x16 (#1), HP 6x13 (#2), HP 10x20 (#3) or Linux 16x32 (#4) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -fw_cfg opt/power-button-enable,string=0 | ||
| + | | disable power button support (from SeaBIOS v14, Qemu v8.2) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -fw_cfg opt/OS64,string=3 | ||
| + | | Bitmask to define the PDC_MODEL_CAPABILITIES on a 64-bit machine: 1=Allow 64-bit OS, 2=Allow 32-bit OS, 3=Allow 32- and 64-bit OS (default), available with SeaBIOS >= v16 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+ While running you can press | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Keyboard shortcut | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ctrl-A + X | ||
| + | | to exit qemu. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ctrl-A + C + ENTER | ||
| + | | Start Qemu monitor. When started with "-serial mon:stdio", the serial port and the QEMU debug port are multiplexed and you can switch between them with this key combination. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ctrl-Alt + F | ||
| + | | switch to fullscreen when using SDL output | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | type "NMI" in qemu monitor (ctrl-A + C) | ||
| + | | to trigger HPPA TOC (transfer-of-control = Reset) button switch | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Examples on how to start the emulator == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * qemu-system-hppa -snapshot -m 512 -device lsi,id=scsi0 -device scsi-hd,drive=drive0,bus=scsi0.0,channel=0,scsi-id=5,lun=0,bootindex=2 -drive file=hdd5.img,if=none,id=drive0 -device scsi-hd,drive=drive1,bus=scsi0.0,channel=0,scsi-id=6,lun=0,bootindex=1 -drive file=hdd2img,if=none,id=drive1 -accel tcg,thread=multi -serial mon:stdio | ||
| + | * qemu-system-hppa -drive file=hdd.img -nographic -serial mon:stdio -accel tcg,thread=multi -smp cpus=2 -drive file=hdd2-.img -boot menu=on -boot order=h | ||
| + | * qemu-system-hppa -boot d -m 512 -drive file=disk.img,format=qcow2 -netdev tap,id=nic1,script=/etc/qemu-ifup -cdrom /opt/iso/HPUX_10.20.iso -device tulip,netdev=nic1,mac=01:00:11:00:00:02 -serial telnet:0.0.0.0:8001,server,nowait -monitor stdio -nographic | ||
| + | * qemu-system-hppa -drive file=../qemu-images/hdd.img -kernel vmlinux -append "root=/dev/sda5 cryptomgr.notests panic=-1" -serial mon:stdio -nographic -accel tcg,thread=multi -smp cpus=3 -netdev bridge,id=hn0,br=virbr0,helper=./qemu-bridge-helper -device tulip,netdev=hn0,id=nic1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | == QEMU special emulated assembler statements == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The emulated guest may use specific asssembler statements to control the qemu emulator: | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+ Standard qemu options: | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Assembler mnemonic | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | .word 0xfffdead0 | ||
| + | | immediately halt the emulator, similiar to turning the machine off | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | .word 0xfffdead1 | ||
| + | | reset machine | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | .word 0xfffdead2 | ||
| + | | restore original (pre-interrupt) values back into shadow registers, used by SeaBIOS when executing NMI instruction in qemu | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | or %r10,%r10,%r10 | ||
| + | | idle loop; wait for interrupt | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | or %r31,%r31,%r31 | ||
| + | | death loop; offline cpu (currently implemented for idle loop). | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+ Qemu standard debugging options: | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Qemu command line option | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Environment variable | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -d item[,...] | ||
| + | | QEMU_LOG e.g in_asm,out_asm | ||
| + | | enable logging of specified items (use '-d help' for a list of items) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | -dfilter 0..0xfffff | ||
| + | | QEMU_DFILTER | ||
| + | | filter logging based on given address range | ||
| + | |} | ||
== How to build QEMU from source == | == How to build QEMU from source == | ||
| − | Check out the [https:// | + | Check out the [https://gitlab.com/qemu-project/qemu qemu git tree] |
| + | |||
| + | '''IMPORTANT:''' | ||
| + | If you plan to run the qemu-user static binary on Debian-11 or below, you NEED to apply this patch: | ||
| + | https://github.com/hdeller/qemu-hppa/commit/540e8fb618e66b4c172cc528c12580bb09e301b6 | ||
| + | (linux-user: handle binfmt-misc P flag as a separate exe name) | ||
Run configure, e.g. | Run configure, e.g. | ||
| Line 36: | Line 189: | ||
Run "make" | Run "make" | ||
| − | == How to run QEMU with Debian-10 installer image == | + | == Linux == |
| + | |||
| + | * Linux kernel >= 4.14 runs best, with initial optimizations added for kernels >= 4.9. | ||
| + | * Prefer the Tulip NIC, then e1000 over the rtl8129 card. The latter gives irq issues with Dino emulation. | ||
| + | * If you try to boot older Linux install CDs (Debian-5, Debian-8, Debian-9), you may need to start qemu with '''"-boot menu=on"''', and then change the kernel console option to '''"console=ttyS0"''' (serial port) instead of "console=tty0" (terminal). Then switch in GUI to the "serial0" device to see console. Alternatively start without graphical console, e.g. with '''"-nographic"'''- | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Ready-to-run Debian Linux QEMU images for parisc === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Download Debian hard disc image: | ||
| + | wget http://dellerweb.de/qemu/debian-12-hdd-2023.img.bz2 | ||
| + | or | ||
| + | wget http://dellerweb.de/qemu/debian-10-hdd.img.bz2 | ||
| + | Unzip image: | ||
| + | bunzip2 debian-12-hdd-2023.img.bz2 | ||
| + | Run qemu: | ||
| + | qemu-system-hppa -drive file=debian-12-hdd-2023.img -nographic -serial mon:stdio -accel tcg,thread=multi -smp cpus=4 | ||
| + | Log in as '''root''', root password is "'''rootme'''" | ||
| + | |||
| + | If a key is missing while running apt-update, do: | ||
| + | apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys <key> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === How to run QEMU with Debian-10 installer image === | ||
* Create a virtual hard disc once: | * Create a virtual hard disc once: | ||
qemu-img create -f qcow2 hdd.img 50G | qemu-img create -f qcow2 hdd.img 50G | ||
* download a Linux install image, e.g. | * download a Linux install image, e.g. | ||
| − | ** for debian: | + | ** for debian: http://backup.parisc-linux.org/debian-cd/debian-11.0.0-hppa-NETINST-1.iso |
** for gentoo: http://distfiles.gentoo.org/releases/hppa/autobuilds/ | ** for gentoo: http://distfiles.gentoo.org/releases/hppa/autobuilds/ | ||
* Start emulator with the installer image once: | * Start emulator with the installer image once: | ||
| − | + | qemu-system-hppa -drive file=hdd.img -drive file=debian-11.0.0-hppa-NETINST-1.iso,media=cdrom -boot order=d -accel tcg,thread=multi -smp cpus=4 -serial mon:stdio -nographic | |
* Choose typical installation options, the defaults are OK. | * Choose typical installation options, the defaults are OK. | ||
| − | |||
* Shut down virtual machine after installation | * Shut down virtual machine after installation | ||
* Start emulator with installed operating system any time: | * Start emulator with installed operating system any time: | ||
| − | + | qemu-system-hppa -drive file=hdd.img -nographic -serial mon:stdio -accel tcg,thread=multi -smp cpus=4 | |
| − | + | === How to create chroot for linux-user === | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | Exampled for debian: |
| + | a=armhf && debootstrap --arch=$a --include=busybox,gcc,gnupg --keyring=/usr/share/keyrings/debian-archive-keyring.gpg --foreign sid $a-chroot http://deb.debian.org/ | ||
| + | debootstrap --arch=ppc64el --include=busybox --foreign sid ppc64el-chroot | ||
| + | debootstrap --arch=alpha --include=busybox --keyring=/usr/share/keyrings/debian-ports-archive-keyring.gpg --foreign sid alpha-chroot http://ftp.ports.debian.org/debian-ports/ | ||
| + | a=powerpc && debootstrap --arch=$a --include=busybox --keyring=/usr/share/keyrings/debian-ports-archive-keyring.gpg --foreign sid $a-chroot http://ftp.ports.debian.org/debian-ports/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | cp /etc/passwd, group, shells target/etc | ||
| + | echo armhf-chroot > etc/debian_chroot | ||
| − | + | === Gentoo Linux === | |
| − | + | * From https://www.gentoo.org/downloads/#hppa download the Minimal installation CD or the hppa32 netboot image (lif file) | |
| − | + | * Start qemu with "-cdrom <isofile>", or the lif file with "-drive file=<lif-file>", e.g. | |
| − | * - | + | qemu-system-hppa -drive file=gentoo-2020-hppa-netboot.lif -accel tcg,thread=multi -smp cpus=2 -nographic |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | == HP-UX == |
| − | * | + | * You will need a set of HP-UX PA-RISC installation CD-ROMS or DVDs |
| − | * The "INTERRUPT KEY" mentioned sometimes by HP-UX can be emulated with the "Ctrl-\" key combination | + | ** starting from [https://www.openpa.net/hp-ux_unix.html#hpux11i HP-UX 10.x up to 11.11 (11i v1)] |
| − | * In case you lost the HP-UX root password, boot at ISL 'hpux -is' and then give a new password with running "passwd". | + | ** only PA-RISC installation medias are supported. CDs for Itanium-2 based HP machines are NOT supported. |
| + | ** you may copy those CDs to ISO files for usage with qemu. | ||
| + | ** please support us by buying from [https://parisc.wiki.kernel.org/index.php/Main_Page#Our_sponsors our sponsors]. | ||
| + | * '''NOTE''': Please '''keep the default screen resolution of 1280x1024 pixels'''. HP-UX may crash if you increase the width, or in graphical environment (with dtwm) the mouse won't be able to reach any line >= 1146 pxels. | ||
| + | * You probably won't be able to boot an original HP-UX installed hard disc image coming from a physical machine other than a B160L. The reason is, that the HP-UX kernel from the other machine has drivers built-in and won't recognize the SCSI and network in the emulated virtual machine. | ||
| + | * LASI NIC emulation and NCR 710 emulation is needed in order to be able to boot older HP-UX releases. | ||
| + | * [https://astr0baby.wordpress.com/2019/04/28/running-hp-ux-11-11-on-qemu-system-hp Astrobaby wrote about his test results.] | ||
| + | * Hints: | ||
| + | ** The "INTERRUPT KEY" mentioned sometimes by HP-UX can be emulated with the "Ctrl-\" key combination | ||
| + | ** In case you lost the HP-UX root password, boot at ISL 'hpux -is' and then give a new password with running "passwd" (you need to use the "-boot menu=on" qemu option) | ||
| + | ** When booting HP-UX may show strange characters instead of brackets - just delete the file /etc/kbdlang, reboot and choose PS2_DIN_US language | ||
| + | * How to start X11, CDE or dtwm | ||
| + | ** CDE Login: init 4 | ||
| + | ** CDE desktop: start "xinit", then "/usr/dt/bin/dtsession" | ||
| + | ** X11: startx | ||
| + | ** dtwm Window Manager: start "xinit", then run "/usr/dt/bin/dtwm". | ||
| − | + | * How to run full filesystem check: fsck -F vxfs -y -o full | |
| + | * File downloads see https://archive.org/download/hpunix/ | ||
| − | + | HP-UX 9 is the first HP-UX release which does support the PA-RISC CPU. | |
| − | + | HP-UX 9.05 fails when booting the install CD: (reported 2021/05/18) | |
| − | + | Stored message buffer up to panic: | |
| − | + | Floating point coprocessor configured and enabled. | |
| − | + | No BTLB entries found for processor 0 | |
| + | Unsupported module type 0x7 found | ||
| + | |||
| + | System Panic: | ||
| + | B2352A HP-UX (A.09.05) #2: Tue Oct 18 15:46:14 PDT 1994 | ||
| + | panic: (display==0xbc00, flags==0x0) Unable to initialize msus structure | ||
| + | PC-Offset Stack Trace (read across, most recent is 1st): | ||
| + | 0x000ec6f8 0x000d7e3c 0x00081e5c 0x000254c0 | ||
| + | End Of Stack | ||
| + | |||
| + | dumping 0 bytes to dev 0xffffffff, offset 0 ... | ||
| + | Dump failed, returning 5. | ||
| − | + | according to [https://archive.org/stream/bitsavers_hp9000hpuxingHPBASICUX6.2Aug91_5917615/E2040-90001_Using_HP_BASIC_UX_6.2_Aug91_djvu.txt this document] "msus" means "mass storage unit specifier" and "msvs" means "mass storage volume specifier" while the msvs is sometimes called an "msus". I assume HP-UX 9.05 doesn't know how to handle the emulated SCSI PCI card and thus can't access the disc. Remember, a B160L is different to a HP700, and a HP700 had a built-in LASI700 (NCR700) SCSI controller. | |
| − | + | === HP ODE === | |
| + | The HP [[Offline Diagnostic Environment (ODE)]] is a great utility to test the quality of the QEMU emulation. | ||
| + | This is an ongoing effort, see above website for details. | ||
| − | + | === HP-UX 9.x === | |
| + | This does not work yet. Mostly due to missing qemu drivers. For here for some notes about how to install [[HPUX-9]]. | ||
== NetBSD == | == NetBSD == | ||
| − | + | Relevant NetBSD/hppa links: | |
| + | * Daily install images: https://nycdn.netbsd.org/pub/NetBSD-daily/netbsd-9/latest/images/ | ||
| + | * Install images: https://cdn.netbsd.org/pub/NetBSD/install-images/ | ||
| + | * Generic NetBSD/hppa info: http://wiki.netbsd.org/ports/hppa/ | ||
| + | * How to install NetBSD with qemu: http://wiki.netbsd.org/ports/hppa/qemu_hppa/ | ||
| − | + | Please note that at least NetBSD-8 required. | |
| − | + | NetBSD-7 doesn't work, since the NetBSD kernel trap handler code complains about the stack pointer in the trap frame. Reported error is: | |
| − | + | insanity: 'tf->tf_sp >= minsp && tf->tf_sp < maxsp' at trap:556 type 0xf tf 0xe00040 lwp 0xe38140 sp 0xa0 pc 0x200240 | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
(info by Nick Hudson <nick.hudson@gmx.co.uk>) | (info by Nick Hudson <nick.hudson@gmx.co.uk>) | ||
| Line 137: | Line 336: | ||
== Future QEMU work == | == Future QEMU work == | ||
| − | + | Possible enhancements: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
* Add Dino/Lasi serial port | * Add Dino/Lasi serial port | ||
* Harmony sound card in Lasi | * Harmony sound card in Lasi | ||
* Does HP-UX has some kind of "sleep" assembler instruction in it's idle loop which can be used to lower qemu power consumption? | * Does HP-UX has some kind of "sleep" assembler instruction in it's idle loop which can be used to lower qemu power consumption? | ||
| − | * Fix virtio-drivers in SeaBIOS (endianess | + | * Fix virtio-drivers in SeaBIOS (missing endianess conversions, because SeaBIOS is originally only Little-endian for x86) |
| − | + | * Emulate a 712 and/or j5000 machine | |
| − | + | * Emulate built-in LASI SCSI controller instead of PCI SCSI add-on card | |
| − | * Emulate a 712 and/or j5000 | + | |
| − | * Emulate built-in LASI | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
== Screenshots == | == Screenshots == | ||
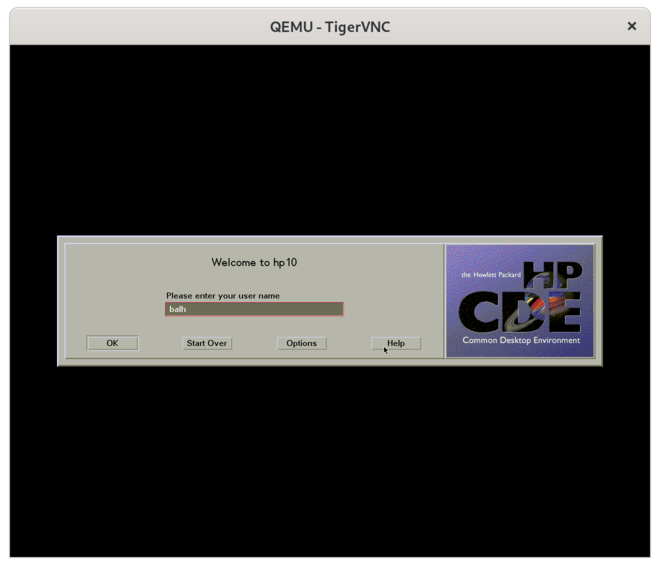
| − | + | === HP-UX CDE graphical Login === | |
| − | + | [[File:hpux-10-cde-login.png|660 px]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | === HP-UX CDE Login | + | |
| − | [[File: | + | |
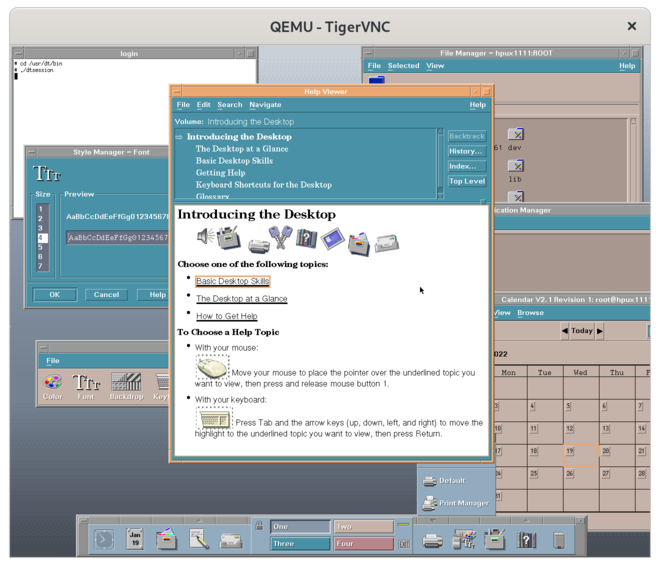
| − | === HP-UX CDE | + | === HP-UX CDE === |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:hpux-10-cde1.png|660 px]] |
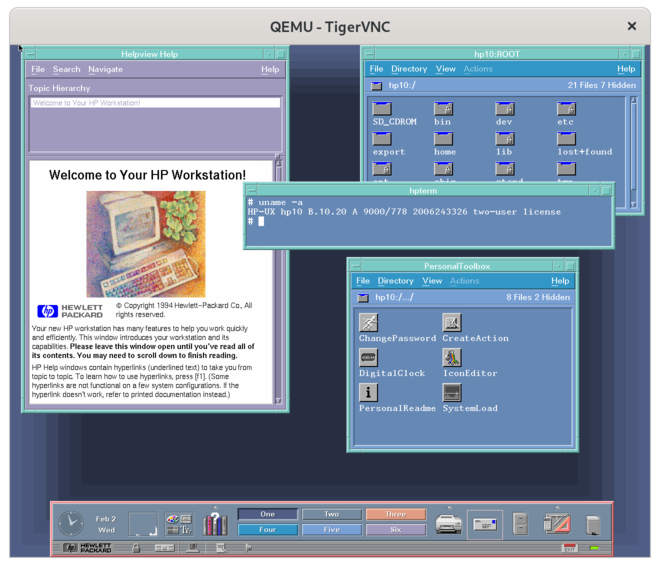
| − | === | + | === HP-UX 10.20 with VUE === |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Hpux-10-vue.png|660 px]] |
Latest revision as of 11:18, 2 April 2024
Contents |
[edit] QEMU for PA-RISC overview
Important: Please run at least QEMU version 8.0.0.
QEMU versions prior to v7.1.0 had various strange bugs. 64-bit CPU emulation requires at least QEMU version 8.2.
QEMU can emulate two different machines:
- a 32-bit HP B160L desktop with up to 16 concurrent PA7100LC CPUs (SMP), and
- a 64-bit HP C3700 workstation with up to 16 concurrent PA8700 CPUs (SMP).
Use the QEMU -machine B160L (for a 32-bit machine) or -machine C3700 (for a 64-bit machine) option to boot. Various operating systems are supported, e.g. Linux, HP-UX and BSD variants. For details please check the sections below. PA-RISC machines need a firmware ("PDC" = Processor Dependend Code), and QEMU comes with a precompiled firmware which is based on a fork of SeaBIOS.
QEMU for PA-RISC has been developed by:
- Richard Henderson: QEMU CPU emulation, QEMU hardware drivers
- Helge Deller: QEMU hardware drivers, SeaBIOS PDC firmware, CPU emulation bug fixes, QEMU linux-user
- Sven Schnelle: Lots of fixes in QEMU and SeaBIOS (SCSI, CPU emulation fixes, SeaBIOS PDC firmware)
QEMU for PA-RISC can be further developed via paid contract from:
- Mark Cave-Ayland: offers paid contract work on QEMU for PA-RISC
[edit] QEMU supported guest operating systems
QEMU does support those operating systems as guests:
- Linux (Debian, Gentoo)
- HP-UX, versions 9.x up to 11.11
- NetBSD, >= 8.0
- NextSTEP
- OSF/MkLinux
[edit] QEMU command line options
| Qemu command line option | |
|---|---|
| -machine C3700 | start a 64-bit C3700 workstation (qemu >= v8.2) |
| -machine B160L | start a 32-bit B160L workstation (default) |
| -smp cpus=4 | define number of CPUs in the guest (maximum CPUs: 32) |
| -m 1G | tell machine to have 1G of RAM memory |
| -accel tcg,thread=multi | always use this to enable parallel tcg (otherwise all guest CPUs run on one host CPU) |
| -boot menu=on | Firmware: enable interactive mode (same as "BOOT PRI IPL") |
| -boot order=c | Firmware: Boot from first hard disc |
| -boot order=d | Firmware: Boot from first CD/DVD |
| -boot order=g-m | Firmware: Boot from SCSI ID0 ("g"), SCSI ID1 ("h"), ... SCSI ID7 ("m") |
| -serial mon:stdio | multiplex serial console to stdout (you want to enable this option!) |
| -nographic | disable artist graphic card emulation, so no graphics output |
| -display sdl | if you need graphics you should prefer SDL display output if your run Qemu < v2.0. In previous qemu versions, GTK had a bug which slows down output. |
| -vnc :1 | start graphics output on VNC output, connect to hostname:1 with any VNC viewer |
| --nodefaults | create an empty machine without default SCSI or network controller (qemu >= v8.2). Add "-serial mon:stdio" to get a serial console, otherwise no output will be visible. |
| Qemu command line option | |
|---|---|
| -global artist.width=800 -global artist.height=600 |
set Artist graphic card to 800x600 pixel |
| -fw_cfg opt/pdc_debug,string=255 | enable all firmware debug infos (1: show PDC calls, 2: show IODC calls) |
| -fw_cfg opt/hostid,string=334455 | set the hostid to 334455 (instead of the default value 2006243326). Visible in Linux in /proc/cpuinfo, and with "uname -i" in HP/UX |
| -fw_cfg opt/console,string=[serial or graphics] | set default firmware output method to serial or graphics console. When selecting serial, you need to add e.g. "-serial mon:stdio" too. |
| -fw_cfg opt/font,string=[1-4] | select default graphics font: HP 8x16 (#1), HP 6x13 (#2), HP 10x20 (#3) or Linux 16x32 (#4) |
| -fw_cfg opt/power-button-enable,string=0 | disable power button support (from SeaBIOS v14, Qemu v8.2) |
| -fw_cfg opt/OS64,string=3 | Bitmask to define the PDC_MODEL_CAPABILITIES on a 64-bit machine: 1=Allow 64-bit OS, 2=Allow 32-bit OS, 3=Allow 32- and 64-bit OS (default), available with SeaBIOS >= v16 |
| Keyboard shortcut | |
|---|---|
| ctrl-A + X | to exit qemu. |
| ctrl-A + C + ENTER | Start Qemu monitor. When started with "-serial mon:stdio", the serial port and the QEMU debug port are multiplexed and you can switch between them with this key combination. |
| ctrl-Alt + F | switch to fullscreen when using SDL output |
| type "NMI" in qemu monitor (ctrl-A + C) | to trigger HPPA TOC (transfer-of-control = Reset) button switch |
[edit] Examples on how to start the emulator
- qemu-system-hppa -snapshot -m 512 -device lsi,id=scsi0 -device scsi-hd,drive=drive0,bus=scsi0.0,channel=0,scsi-id=5,lun=0,bootindex=2 -drive file=hdd5.img,if=none,id=drive0 -device scsi-hd,drive=drive1,bus=scsi0.0,channel=0,scsi-id=6,lun=0,bootindex=1 -drive file=hdd2img,if=none,id=drive1 -accel tcg,thread=multi -serial mon:stdio
- qemu-system-hppa -drive file=hdd.img -nographic -serial mon:stdio -accel tcg,thread=multi -smp cpus=2 -drive file=hdd2-.img -boot menu=on -boot order=h
- qemu-system-hppa -boot d -m 512 -drive file=disk.img,format=qcow2 -netdev tap,id=nic1,script=/etc/qemu-ifup -cdrom /opt/iso/HPUX_10.20.iso -device tulip,netdev=nic1,mac=01:00:11:00:00:02 -serial telnet:0.0.0.0:8001,server,nowait -monitor stdio -nographic
- qemu-system-hppa -drive file=../qemu-images/hdd.img -kernel vmlinux -append "root=/dev/sda5 cryptomgr.notests panic=-1" -serial mon:stdio -nographic -accel tcg,thread=multi -smp cpus=3 -netdev bridge,id=hn0,br=virbr0,helper=./qemu-bridge-helper -device tulip,netdev=hn0,id=nic1
[edit] QEMU special emulated assembler statements
The emulated guest may use specific asssembler statements to control the qemu emulator:
| Assembler mnemonic | |
|---|---|
| .word 0xfffdead0 | immediately halt the emulator, similiar to turning the machine off |
| .word 0xfffdead1 | reset machine |
| .word 0xfffdead2 | restore original (pre-interrupt) values back into shadow registers, used by SeaBIOS when executing NMI instruction in qemu |
| or %r10,%r10,%r10 | idle loop; wait for interrupt |
| or %r31,%r31,%r31 | death loop; offline cpu (currently implemented for idle loop). |
| Qemu command line option | Environment variable | |
|---|---|---|
| -d item[,...] | QEMU_LOG e.g in_asm,out_asm | enable logging of specified items (use '-d help' for a list of items) |
| -dfilter 0..0xfffff | QEMU_DFILTER | filter logging based on given address range |
[edit] How to build QEMU from source
Check out the qemu git tree
IMPORTANT: If you plan to run the qemu-user static binary on Debian-11 or below, you NEED to apply this patch: https://github.com/hdeller/qemu-hppa/commit/540e8fb618e66b4c172cc528c12580bb09e301b6 (linux-user: handle binfmt-misc P flag as a separate exe name)
Run configure, e.g.
- (for system emulation) ./configure --target-list=hppa-softmmu --enable-numa
- (for user emulation) ./configure --target-list=hppa-linux-user --disable-stack-protector --prefix=/home/qemu-hppa/chroot-unstable --interp-prefix=/home/qemu-hppa/chroot-unstable --static
Run "make"
[edit] Linux
- Linux kernel >= 4.14 runs best, with initial optimizations added for kernels >= 4.9.
- Prefer the Tulip NIC, then e1000 over the rtl8129 card. The latter gives irq issues with Dino emulation.
- If you try to boot older Linux install CDs (Debian-5, Debian-8, Debian-9), you may need to start qemu with "-boot menu=on", and then change the kernel console option to "console=ttyS0" (serial port) instead of "console=tty0" (terminal). Then switch in GUI to the "serial0" device to see console. Alternatively start without graphical console, e.g. with "-nographic"-
[edit] Ready-to-run Debian Linux QEMU images for parisc
Download Debian hard disc image:
wget http://dellerweb.de/qemu/debian-12-hdd-2023.img.bz2
or
wget http://dellerweb.de/qemu/debian-10-hdd.img.bz2
Unzip image:
bunzip2 debian-12-hdd-2023.img.bz2
Run qemu:
qemu-system-hppa -drive file=debian-12-hdd-2023.img -nographic -serial mon:stdio -accel tcg,thread=multi -smp cpus=4
Log in as root, root password is "rootme"
If a key is missing while running apt-update, do:
apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys <key>
[edit] How to run QEMU with Debian-10 installer image
- Create a virtual hard disc once:
qemu-img create -f qcow2 hdd.img 50G
- download a Linux install image, e.g.
- Start emulator with the installer image once:
qemu-system-hppa -drive file=hdd.img -drive file=debian-11.0.0-hppa-NETINST-1.iso,media=cdrom -boot order=d -accel tcg,thread=multi -smp cpus=4 -serial mon:stdio -nographic
- Choose typical installation options, the defaults are OK.
- Shut down virtual machine after installation
- Start emulator with installed operating system any time:
qemu-system-hppa -drive file=hdd.img -nographic -serial mon:stdio -accel tcg,thread=multi -smp cpus=4
[edit] How to create chroot for linux-user
Exampled for debian:
a=armhf && debootstrap --arch=$a --include=busybox,gcc,gnupg --keyring=/usr/share/keyrings/debian-archive-keyring.gpg --foreign sid $a-chroot http://deb.debian.org/ debootstrap --arch=ppc64el --include=busybox --foreign sid ppc64el-chroot debootstrap --arch=alpha --include=busybox --keyring=/usr/share/keyrings/debian-ports-archive-keyring.gpg --foreign sid alpha-chroot http://ftp.ports.debian.org/debian-ports/ a=powerpc && debootstrap --arch=$a --include=busybox --keyring=/usr/share/keyrings/debian-ports-archive-keyring.gpg --foreign sid $a-chroot http://ftp.ports.debian.org/debian-ports/ cp /etc/passwd, group, shells target/etc echo armhf-chroot > etc/debian_chroot
[edit] Gentoo Linux
- From https://www.gentoo.org/downloads/#hppa download the Minimal installation CD or the hppa32 netboot image (lif file)
- Start qemu with "-cdrom <isofile>", or the lif file with "-drive file=<lif-file>", e.g.
qemu-system-hppa -drive file=gentoo-2020-hppa-netboot.lif -accel tcg,thread=multi -smp cpus=2 -nographic
[edit] HP-UX
- You will need a set of HP-UX PA-RISC installation CD-ROMS or DVDs
- starting from HP-UX 10.x up to 11.11 (11i v1)
- only PA-RISC installation medias are supported. CDs for Itanium-2 based HP machines are NOT supported.
- you may copy those CDs to ISO files for usage with qemu.
- please support us by buying from our sponsors.
- NOTE: Please keep the default screen resolution of 1280x1024 pixels. HP-UX may crash if you increase the width, or in graphical environment (with dtwm) the mouse won't be able to reach any line >= 1146 pxels.
- You probably won't be able to boot an original HP-UX installed hard disc image coming from a physical machine other than a B160L. The reason is, that the HP-UX kernel from the other machine has drivers built-in and won't recognize the SCSI and network in the emulated virtual machine.
- LASI NIC emulation and NCR 710 emulation is needed in order to be able to boot older HP-UX releases.
- Astrobaby wrote about his test results.
- Hints:
- The "INTERRUPT KEY" mentioned sometimes by HP-UX can be emulated with the "Ctrl-\" key combination
- In case you lost the HP-UX root password, boot at ISL 'hpux -is' and then give a new password with running "passwd" (you need to use the "-boot menu=on" qemu option)
- When booting HP-UX may show strange characters instead of brackets - just delete the file /etc/kbdlang, reboot and choose PS2_DIN_US language
- How to start X11, CDE or dtwm
- CDE Login: init 4
- CDE desktop: start "xinit", then "/usr/dt/bin/dtsession"
- X11: startx
- dtwm Window Manager: start "xinit", then run "/usr/dt/bin/dtwm".
- How to run full filesystem check: fsck -F vxfs -y -o full
- File downloads see https://archive.org/download/hpunix/
HP-UX 9 is the first HP-UX release which does support the PA-RISC CPU. HP-UX 9.05 fails when booting the install CD: (reported 2021/05/18)
Stored message buffer up to panic:
Floating point coprocessor configured and enabled.
No BTLB entries found for processor 0
Unsupported module type 0x7 found
System Panic:
B2352A HP-UX (A.09.05) #2: Tue Oct 18 15:46:14 PDT 1994
panic: (display==0xbc00, flags==0x0) Unable to initialize msus structure
PC-Offset Stack Trace (read across, most recent is 1st):
0x000ec6f8 0x000d7e3c 0x00081e5c 0x000254c0
End Of Stack
dumping 0 bytes to dev 0xffffffff, offset 0 ...
Dump failed, returning 5.
according to this document "msus" means "mass storage unit specifier" and "msvs" means "mass storage volume specifier" while the msvs is sometimes called an "msus". I assume HP-UX 9.05 doesn't know how to handle the emulated SCSI PCI card and thus can't access the disc. Remember, a B160L is different to a HP700, and a HP700 had a built-in LASI700 (NCR700) SCSI controller.
[edit] HP ODE
The HP Offline Diagnostic Environment (ODE) is a great utility to test the quality of the QEMU emulation. This is an ongoing effort, see above website for details.
[edit] HP-UX 9.x
This does not work yet. Mostly due to missing qemu drivers. For here for some notes about how to install HPUX-9.
[edit] NetBSD
Relevant NetBSD/hppa links:
- Daily install images: https://nycdn.netbsd.org/pub/NetBSD-daily/netbsd-9/latest/images/
- Install images: https://cdn.netbsd.org/pub/NetBSD/install-images/
- Generic NetBSD/hppa info: http://wiki.netbsd.org/ports/hppa/
- How to install NetBSD with qemu: http://wiki.netbsd.org/ports/hppa/qemu_hppa/
Please note that at least NetBSD-8 required. NetBSD-7 doesn't work, since the NetBSD kernel trap handler code complains about the stack pointer in the trap frame. Reported error is:
insanity: 'tf->tf_sp >= minsp && tf->tf_sp < maxsp' at trap:556 type 0xf tf 0xe00040 lwp 0xe38140 sp 0xa0 pc 0x200240
(info by Nick Hudson <nick.hudson@gmx.co.uk>)
[edit] OSF/MkLinux
Download at ftp://ftp.cirr.com/pub/hppa/mklinux/ The file root_ext2_g.dd.bin.gz doesn't cleanly decompress.. so I did a gzip -dc into root_ext2_g.dd.bin.
MkLinux sources: https://github.com/slp/osfmk-mklinux
qemu-system-hppa -boot c -drive if=scsi,bus=0,index=3,file=root_ext2_g.dd.bin,format=raw \
-serial mon:stdio -nographic -m 128
It boots, but fails during device detection because Qemu currently emulates a B160, while MkLinux expects a HP700. So it fails to see the LASI chip below the GSC bridge.
NVM bootdata Bad Checksum (0)
OSF Mach boot
: /mach
text (0x95618) at 0x11000
data (0x48594) at 0xa8000
Mach 3.0 VERSION(PMK1.1): cb <pmk1_1>; Wed Nov 26 17:20:37 MET 1997; mach_kernel/PRODUCTION (cameleon)
HP9000/
unknown machine type 0x502
good luck :-)
, 0K Icache, 0K Dcache, 256 entry shared TLB)
Warning: unsupported module at ffc00000 (type:7 svers:0 hvers:50)
Stack Trace (depth=1):
0x00084d68
End of Stack
(info by Jason Stevens <neozeed@gmail.com>)
[edit] Future QEMU work
Possible enhancements:
- Add Dino/Lasi serial port
- Harmony sound card in Lasi
- Does HP-UX has some kind of "sleep" assembler instruction in it's idle loop which can be used to lower qemu power consumption?
- Fix virtio-drivers in SeaBIOS (missing endianess conversions, because SeaBIOS is originally only Little-endian for x86)
- Emulate a 712 and/or j5000 machine
- Emulate built-in LASI SCSI controller instead of PCI SCSI add-on card